Vitamin D Milk Nutrition
Top 10 High Vitamin D Foods

Powered by USDA Nutrition Data

Vitamin D is an essential vitamin required by the body for the absorption of calcium, bone development, immune functioning and alleviation of inflammation. (1)
A deficiency of Vitamin D can lead to rickets, a weakened immune system, increased cancer risk, poor hair growth and osteomalacia. (1)
Excess vitamin D can cause the body to absorb too much calcium, leading to increased risk of heart disease and kidney stones. (1)
The current U.S. Daily Value (%DV) for vitamin D is 20μg (micrograms) and the toxicity threshold is thought to be 250 to 1000 μg/day. (1)
Sometimes vitamin D values are given in IU (International Units). When this is the case remember that 1μg=40IU for Vitamin D. (1)
Vitamin D is fat soluble, which means you need to eat fat to absorb it. Foods high in vitamin D include fish, mushrooms exposed to sunlight, fortified milk, fortified milk substitutes, fortified tofu, fortified yogurt, fortified breakfast cereals, fortified orange juice, pork chops, and eggs.
Vitamin D is also made by the body when skin is exposed sunlight and is therefore called the sunshine vitamin. This accounts for approximately 90% of our total vitamin D, with only 10% coming from food. Depending on where you live, 20 minutes of sun exposure a day is enough to meet your vitamin D requirements.
Below is a list of the top 10 foods highest in vitamin D by common serving size, for more see the nutrient ranking of 200 foods high in vitamin D.
- Introduction
- High Vitamin D Foods
- Printable
- Foods High in Vitamin D2
- Foods High in Vitamin D3
- Deficiency Risk Factors
- What Fruits and Vegetables are High in Vitamin D?
- Warnings
- About the Data
- Nutrient Ranking Tool
- Related
- Feedback
- References

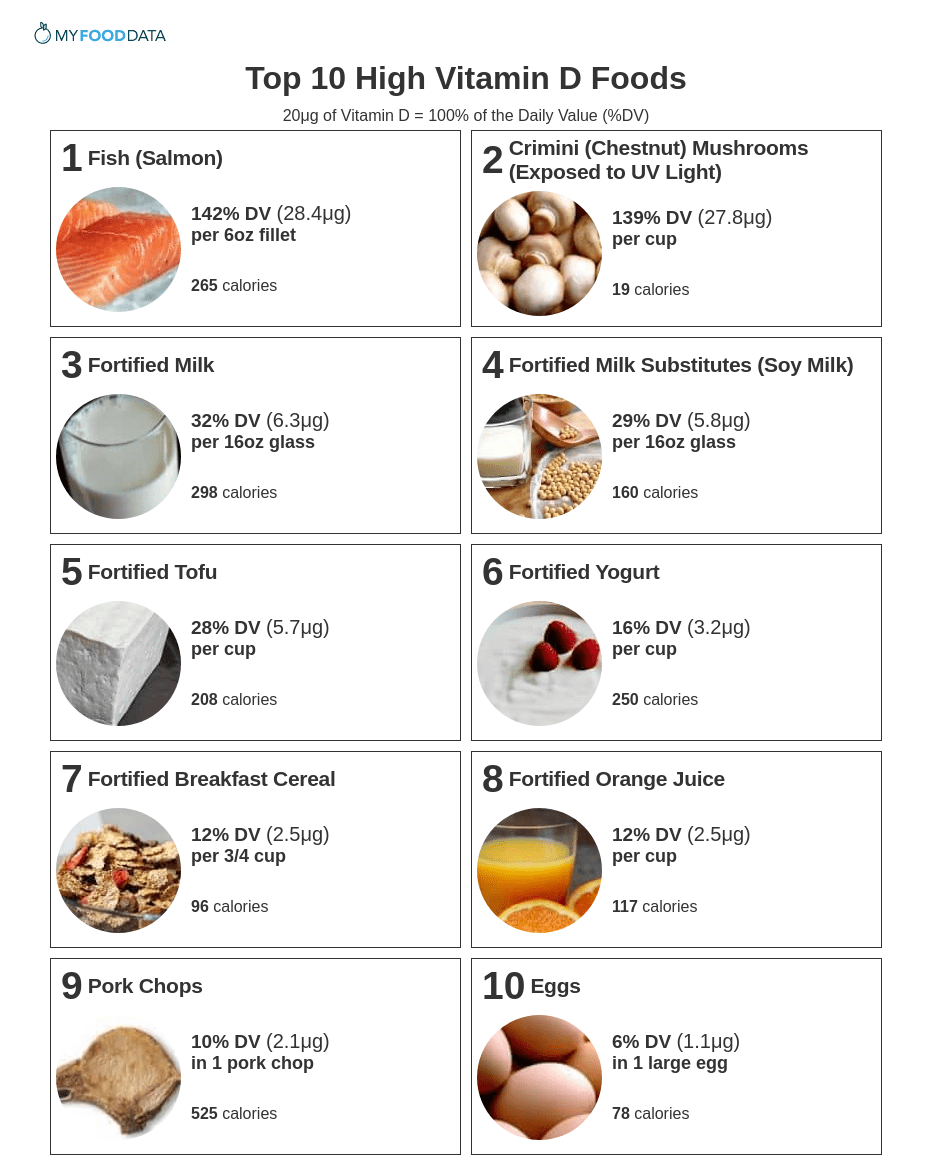
#1: Fish (Salmon)
| Vitamin D per 6oz Fillet | Vitamin D per 100g | Vitamin D per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 28.4μg (142% DV) | 16.7μg (84% DV) | 21.4μg (107% DV) |

#2: Crimini (Chestnut) Mushrooms (Exposed to UV Light)
| Vitamin D per Cup | Vitamin D per 100g | Vitamin D per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 27.8μg (139% DV) | 31.9μg (160% DV) | 290μg (1450% DV) |

#3: Fortified Milk
| Vitamin D per 16oz Glass | Vitamin D per 100g | Vitamin D per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 6.3μg (32% DV) | 1.3μg (7% DV) | 4.3μg (21% DV) |

#4: Fortified Milk Substitutes (Soy Milk)
| Vitamin D per 16oz Glass | Vitamin D per 100g | Vitamin D per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 5.8μg (29% DV) | 1.2μg (6% DV) | 7.3μg (36% DV) |

#5: Fortified Tofu
| Vitamin D per Cup | Vitamin D per 100g | Vitamin D per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 5.7μg (28% DV) | 2.5μg (13% DV) | 5.4μg (27% DV) |

#6: Fortified Yogurt
| Vitamin D per Cup | Vitamin D per 100g | Vitamin D per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 3.2μg (16% DV) | 1.3μg (7% DV) | 2.5μg (13% DV) |

#7: Fortified Breakfast Cereal
| Vitamin D per 3/4 Cup | Vitamin D per 100g | Vitamin D per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 2.5μg (12% DV) | 8.3μg (42% DV) | 5.2μg (26% DV) |

#8: Fortified Orange Juice
| Vitamin D per Cup | Vitamin D per 100g | Vitamin D per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 2.5μg (12% DV) | 1μg (5% DV) | 4.3μg (21% DV) |

#9: Pork Chops
| Vitamin D in 1 Pork Chop | Vitamin D per 100g | Vitamin D per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 2.1μg (10% DV) | 1μg (5% DV) | 0.8μg (4% DV) |

#10: Eggs
| Vitamin D in 1 Large Egg | Vitamin D per 100g | Vitamin D per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 1.1μg (6% DV) | 2.2μg (11% DV) | 2.8μg (14% DV) |
See All 200 Foods High in Vitamin D
 Next ➞
Next ➞
Printable One Page Sheet
Click to Print
Foods High in Vitamin D2
Foods High in Vitamin D3
People at Risk of a Vitamin D Deficiency
- Breastfed Infants Who are Not in the Sun - The amount of vitamin D in breast milk depends on the amount of vitamin D in the mother. However, breast-milk typically does not contain adequate amounts of vitamin D. Be sure infants get some exposure to the sun (at least 10-20 minutes per day) to ensure adequate levels of vitamin D. (1)
- Older Adults - As skin ages it is less and less able to make vitamin D from the sun, so vitamin D has to be attained from foods or supplements. (1)
- People With Little Sun Exposure on the Skin - Wearing sunscreen, or lots of clothing, hampers the production of vitamin D from the sun. (1)
- People with Darker Skin - Melanin, a pigment found in skin, reduces the body's ability to manufacture vitamin D from the sun. (1)
- People who have Problems Absorbing Fat - Vitamin D is fat soluble, which means it is found in fats, and your body has to be able to digest fats in order for you to absorb the vitamin D. (1)
- People Taking Certain Medications
- Steroid Corticosteroid medications used to alleviate inflammation can reduce calcium absorption and impair vitamin D metabolism. (1)
- Weight-loss drugs with orlistat as well as cholesterol-lowering drugs with cholestyramine can reduce the absorption of vitamin D and other fat-soluble vitamins. (1)
- Medicines used to treat epileptic seizures, particularly phenobarbital and phenytoin, interfere with Vitamin D and reduces calcium absorption. (1)
What Fruits and Vegetables are High in Vitamin D?
Vegetables high in vitamin D include mushrooms which have been exposed to sunlight. Other vegan foods high in vitamin D include fortified soy products like tofu, soy milk, and soy yogurt, fortified cereals, and fortified juices.
Unfortunately, no fruits are high in vitamin D, and fortified orange juice is currently the only fruit product commonly sold with vitamin D.
Warnings
Consuming too much vitamin D from food or supplements can lead to anorexia, weight loss, polyuria, heart arrhythmias, kidney stones, and increased risk of heart attacks. Vitamin D cannot reach toxic levels if created naturally from sun exposure. (1)
About the Data
Data for the curated food lists comes from the USDA Food Data Central Repository.
You can check our data against the USDA by clicking the (Source) link at the bottom of each food listing.
Note: When checking data please be sure the serving sizes are the same. In the rare case you find any difference, please contact us and we will fix it right away.
- Foods High in Vitamin D
- Foods Low in Vitamin D
- Vegetarian Foods High in Vitamin D
- Dairy High in Vitamin D
- Breakfast Cereals High in Vitamin D
- Fast Foods High in Vitamin D
View more food groups with the nutrient ranking tool, or see ratios with the nutrient ratio tool.
- Cereals High in Vitamin D
- Dairy Foods High in Vitamin D
- High Calcium Foods
- High Calcium Fruits
- High Calcium Vegetables
- High Vitamin K Foods
- High Potassium Foods
feedback
Data Sources and References
- Office of Dietary Supplements - Vitamin D
- U.S. Agricultural Research Service Food Data Central
MyFoodData provides nutrition data tools and articles to help you organize and understand the foods you eat. Read more...
Source: https://www.myfooddata.com/articles/high-vitamin-D-foods.php







Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar